Spend $50 and get FREE SHIPPING

By now, most people are at least vaguely aware that CBD can help support one’s wellness routine. But not many people know exactly why CBD is so beneficial and how it works in the body.
The secret behind CBD is something called the Endocannabinoid System aka ECS. This sophisticated system is comprised of a series of proteins, receptors, and neurotransmitters throughout your body. The ECS operates independently of every other internal system, with one goal in mind: preserve the balance in your body, i.e., maintain homeostasis.
The ECS is responsible for making sure your body functions the way it should. It’s like a well-designed security system — both monitoring your body’s homeostasis to make sure that everything is balanced, and deploying the proper resources to deal with any problems that arise. For example, when you run, you generate excess amounts of heat. The ECS makes sure you stay cool by prompting the sweat glands to produce sweat, thereby cooling your body and ensuring you don’t overheat — keeping everything in perfect balance.
If you’re looking to take a deeper dive, check out this study published in the US National Library of Medicine that details the emerging research demonstrating the benefits of CBD.
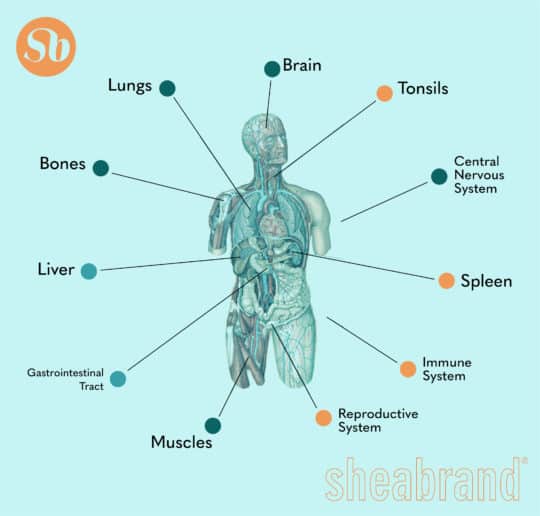
Furthermore, here are some other critical functions in which the ECS plays a role:
There are three elements that comprise the Endocannabinoid System: cannabinoids themselves, cannabinoid receptors, and an enzyme that breaks down and discards cannabinoids.
Cannabinoids are the fuel that powers the entire ECS system. A lack of cannabinoids can cause so, so many issues. If your ECS doesn’t have cannabinoids, it doesn’t have the juice to help you sleep properly, or to release chemicals to calm you down when you’re dealing with anxiety. For further proof, you don’t have to look farther than this study which details the role the cannabinoid system plays in pain management.
Your body produces some cannabinoids naturally. These are called endocannabinoids. Everyone produces different levels of endocannabinoids; unfortunately, some produce so few that they are diagnosed with chronic endocannabinoid deficiency, which can cause major sleep issues, anxiety, pain, inflammation, focus problems and more.

Even worse, we naturally produce fewer cannabinoids as we age, meaning that as we get older, our ECS struggles to function properly.
Luckily, we can supplement our bodies with cannabinoids that come from plants. Just as we take vitamin and mineral supplements to provide our bodies with crucial nutrients, CBD supplements our natural endocannabinoid production. Supplementing our bodies ECS with CBD is something every one of us should be doing every single day if we want to be at our best, especially as you age.
Phytocannabinoids similar to CBD, CBG, CBN and CBC are found in nature and are easily accessed by ingesting plants like broccoli and bok choy, or by using CBD products — hemp is a plant, of course!

All those endo-and-phytocannabinoids have to go somewhere. They are attracted to different types of cannabinoid receptors that act as landing pads. Once the two meet, they trigger functions designed to promote balance and homeostasis throughout the body. Sometimes cannabinoids fit in the receptor like a lock and key and in other cases the cannabinoids do not lock into place but can still interact with receptors.
These receptors are responsible for making the entire ECS function properly. They’re essentially the watchdogs of the ECS — constantly monitoring our bodies and stepping in with crucial efforts to make sure everything stays balanced. If something’s out of whack, they take action.
Receptors take the fuel (cannabinoids), use that fuel to scan the environment and analyze the current situation, and then send signals to the rest of the body to re-establish homeostasis.
CBD receptors exist throughout our bodies, in the cell walls of our organs and tissues. They are, however, perhaps most numerous on the body’s largest organ, the skin, where it affects 130 different functions including collagen production and skin cell regeneration. For more on the profound impact CBD has on our skin, check out the eye-opening findings by Genemarkers, a prominent leader in pharmaceutical research.
This epidermal efficacy is why topical CBD treatments are so effective at treating wounds and dealing with localized pain. It’s also why CBD is becoming a leading skincare ingredient.

Last but not least are metabolic enzymes — an often overlooked aspect of cannabinoids.
These catalysts of the ECS are responsible for waste. That is, ECS enzymes are particularly suited to breaking down and getting rid of any unnecessary or unused cannabinoids in the body. These enzymes keep things neat and tidy in the ECS system, allowing the receptors to more easily and efficiently access the cannabinoids the ECS needs to function.
These enzymes unlock a potential for potent and efficacious drugs and treatments without side effects. Currently, research and development into unlocking the power of these enzymes is happening all over the world, promising to create more precise treatments with fewer side effects.

THC is very similar to another cannabinoid, anandamide, one of the cannabinoids responsible for reward function (i.e., dopamine).
So if you’re ever wondering why you feel a wave of euphoria after hitting a joint, this effect is being created by dopamine in your brain. Both THC and anandamide can provide this hit of relief. And it’s the same reward function that creates the famous “runners high.” But because of the enzymes produced by the ECS, this high doesn’t last as long as if you were smoking THC and thereby constantly feeding the brain with cannabinoids.
Enjoyed this article? You might find this helpful too:
Why Do Cannabinoids Help With Pain?